
Instead, MP3 files use perceptual coding. That means that an MP3 file does not contain 100% of the original audio information. This then enables you to get hundreds of songs on to a CD and it also has opened up a new market over the internet - the download market as download times have been significantly reduced. MP3 gets rid of a lot of the information recorded in a song that our ears are not able to hear and then uses complex algorithms to reduce the file size. MP3 is a digital music format which allows CD tracks to be reduced to around a tenth of their normal size without a significant loss of quality.
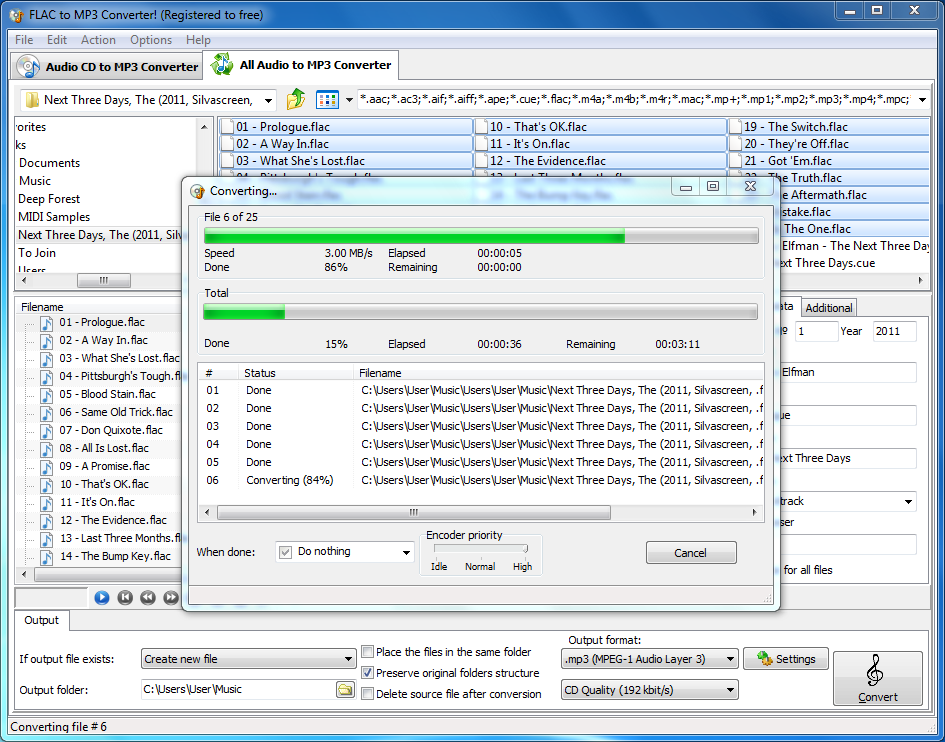
The metadata associated with the audio has been future proofed also to allow new fields to be defined without impacting existing decoders. A FLAC file also contains several data integrity checks in the header file. The main benefits of a FLAC file in addition to it being lossless is that it can be used for streaming, and decoding is fast, allowing for real time decoding to take place. Using FLAC to compress an audio file to approximately 50% of its original size. FLAC is a format that is recommended to those backing up a CD collection because the sound quality will remain high, whereas MP3 compression will result in a deterioration compared to the original. It is a lossless compression type meaning that the compression takes place without data being discarded. VLC media player, MPlayer, Winamp, foobar2000.Free Lossless Audio Codec, or FLAC for short, is an audio compression technique. Windows 10, Android, Blackberry 10 and Jolla devices. For example, an MP3 file created using the setting of 128 kbit/s will result in a file about 1/11 the size of the CD file created from the original audio source. Lossy compression is designed to reduce significantly the amount of data required to represent the audio recording and still sound like a faithful reproduction of the original uncompressed audio. Compared to compressed audio formats, FFmpeg's FLAC implementation was noted to have the fastest and most efficient embedded decoder of any modern lossless audio format. The technical strengths of FLAC compared to other lossless formats lie in its ability to be streamed and decoded quickly, independent of compression level. It is a common audio format for consumer audio streaming or storage and a de facto standard of digital audio compression for the transfer and playback of music on most digital audio players. MPEG-1 or MPEG-2 Audio Layer III, more commonly referred to as MP3, is an audio coding format for digital audio that uses lossy data compression.

Digital audio compressed by FLAC's algorithm can typically be reduced to 50-60% of its original size and decompress to an identical copy of the original audio data. FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec) is an audio coding format for lossless compression of digital audio and is also the name of the reference codec implementation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
